The Evolution of Space Transportation: From Space Shuttles to Soyuz

Space exploration has always captivated the imagination of humanity, pushing the boundaries of what we can achieve as a species. Throughout history, we have witnessed remarkable advancements in space transportation, from the monumental Apollo missions to the groundbreaking Space Shuttle program. However, as with any technology, the space shuttles eventually reached the end of their operational life. In this article, we will explore the retirement of the Space Shuttle program and the subsequent reliance on the Russian Soyuz spacecraft by NASA. Let’s delve into the fascinating journey of space transportation and the reasons behind these pivotal shifts.
The Rise and Fall of the Space Shuttle Program
The Birth of the Space Shuttle
In 1972, NASA unveiled the Space Shuttle program, introducing a revolutionary concept in space travel. Unlike previous missions, the Space Shuttle was designed to be a reusable spacecraft, capable of carrying large satellites to and from orbit. With this ambitious project, NASA aimed to create a “space truck” that could facilitate the construction of a United States space station in low Earth orbit by the early 1990s.
The Space Shuttle’s Mission and Achievements
The Space Shuttle program consisted of three orbiters: Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour. Each orbiter was designed to undertake at least 100 missions, showcasing the remarkable versatility and endurance of these spacecraft. The Space Shuttle’s primary goal was to transport crew members and cargo to the International Space Station (ISS) and deploy various satellites into orbit.
One of the most significant accomplishments of the Space Shuttle program was its role in the assembly of the ISS. The Space Shuttle orbiters played a crucial part in delivering modules and equipment, contributing to the construction of this remarkable international collaboration in space exploration.
The Costly Reality: Retirement of the Space Shuttle Program
As awe-inspiring as the Space Shuttle program was, it was not without its challenges. The primary reason for retiring the program in 2011 was its astronomical cost. Launching a single Space Shuttle mission came with an average price tag of nearly $1.5 billion, making it financially unsustainable in the long run.
The expenses associated with maintaining and refurbishing the Space Shuttle fleet, along with the high risks involved, led NASA to make the difficult decision to retire these iconic spacecraft. However, their retirement marked the beginning of a new era in space transportation, with NASA turning to the Russian Soyuz spacecraft for crewed missions.
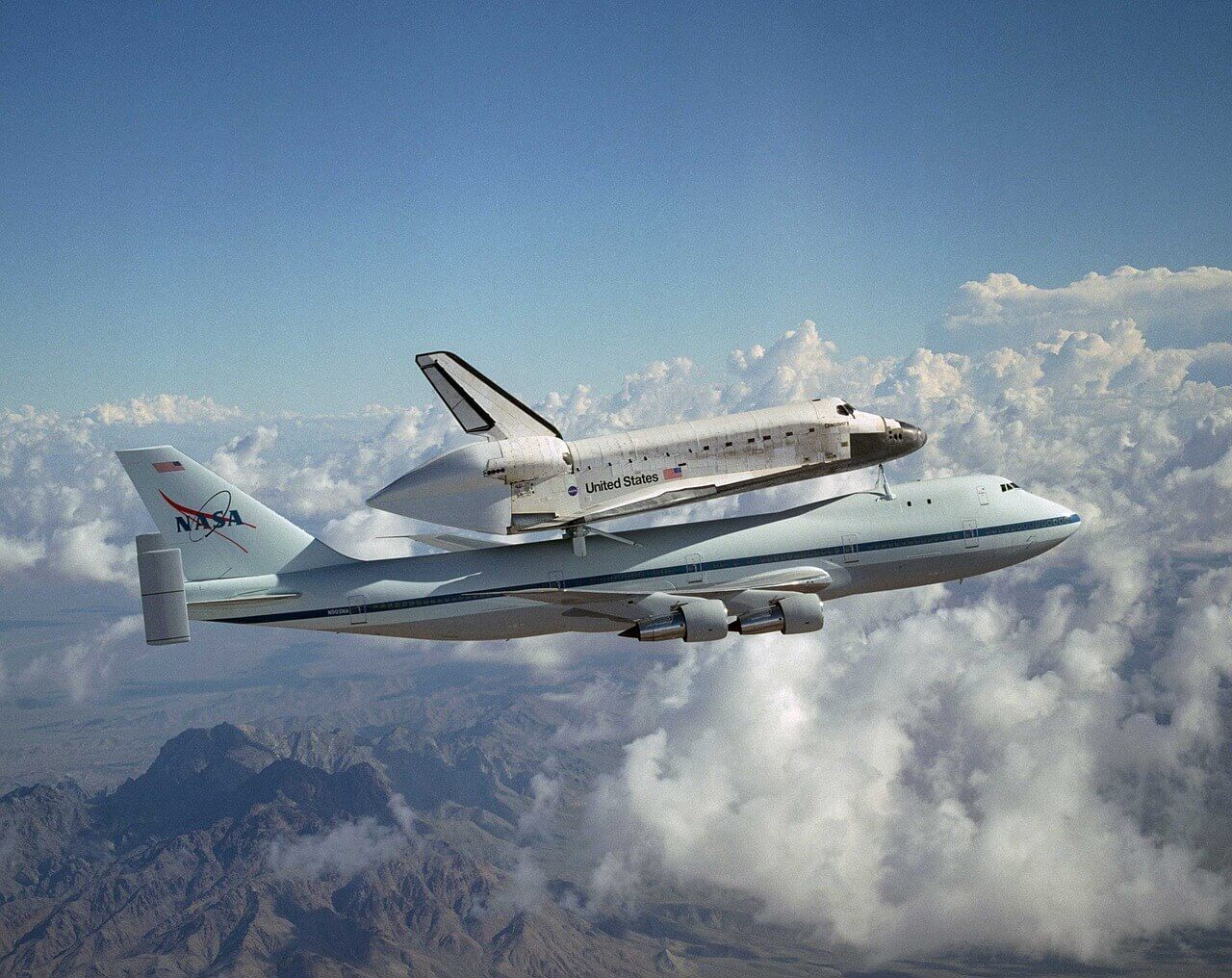

Transition to the Russian Soyuz Spacecraft
Dependency on Soyuz: A Temporary Solution
With the retirement of the Space Shuttle program, NASA found itself in a position of dependence on the Russian Soyuz spacecraft for transporting astronauts to and from the ISS. While this arrangement was meant to be temporary, it highlighted the need for NASA to develop a new generation of spacecraft to regain its independence in crewed space missions.
The Soyuz Spacecraft: A Reliable Workhorse
The Soyuz spacecraft, developed by the Russian space agency Roscosmos, has a long-standing reputation for its reliability and safety. It has been in operation since the 1960s and has become the backbone of crewed missions to the ISS.
The Soyuz spacecraft consists of three modules: the Orbital Module, the Descent Module, and the Instrumentation Module. Its iconic design has remained largely unchanged over the years, a testament to its effectiveness and efficiency in transporting astronauts safely to and from space.
Collaboration Amidst Competition: The Soyuz and Commercial Crew Program
While NASA relied on the Soyuz spacecraft for crewed missions, it also recognized the importance of fostering its own capabilities in space transportation. This led to the inception of the Commercial Crew Program, an initiative aimed at developing new spacecraft within the United States.
Through partnerships with private companies like SpaceX and Boeing, NASA sought to revive its ability to launch astronauts from American soil. This collaboration between government and industry has paved the way for a new era of space transportation, with spacecraft like SpaceX’s Crew Dragon and Boeing’s Starliner poised to take the baton from the Soyuz spacecraft.
The Future of Space Transportation
From Soyuz to Starships: Advancements on the Horizon
As we look ahead, the future of space transportation holds exciting possibilities. With the emergence of commercial spaceflight companies and the development of next-generation spacecraft, we are witnessing a transformative shift in how we explore and utilize space.
SpaceX, led by visionary entrepreneur Elon Musk, has been at the forefront of this revolution. Their Starship spacecraft, currently in development, aims to revolutionize space travel with its reusable design and capability to transport large numbers of passengers and cargo to destinations beyond Earth’s orbit.
SpaceX has been conducting several flight tests of the Starship, and the latest video update from September 4, 2023, shows the final phase of preparations for the spacecraft.
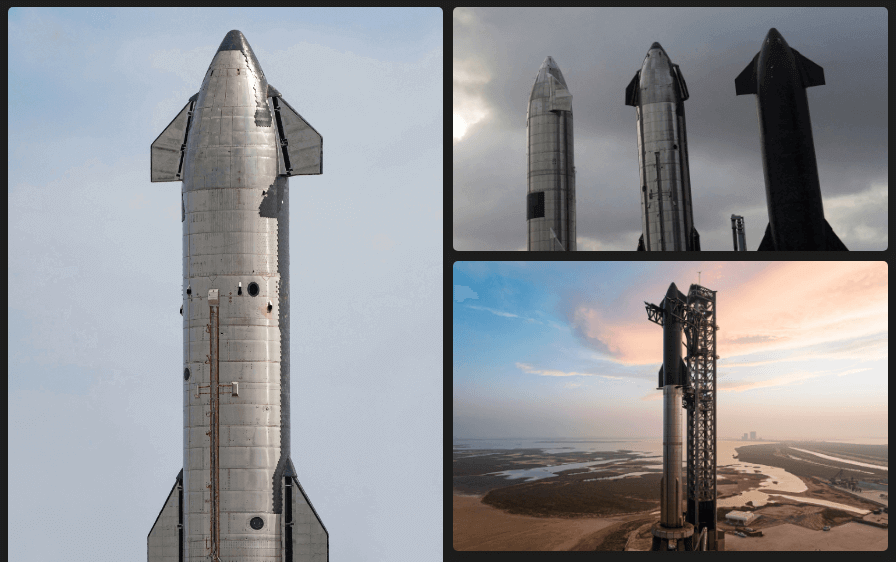
The Starship spacecraft is expected to revolutionize space travel with its capability to transport people and cargo to the Moon and beyond. It is designed to be fully reusable, reducing the cost of space exploration and transportation. Additionally, Starship’s Super Heavy booster will be capable of lifting over 100 tons into orbit.
SpaceX is not alone in its efforts to revolutionize space travel. Companies like Blue Origin, Boeing, United Launch Alliance, and Virgin Galactic are all developing their own spacecraft with the goal of providing reliable access to space for a variety of applications.
These advancements come at an exciting time in the history of space exploration as we look ahead towards a new era of exploration and discovery. With these new capabilities, we can begin to explore further than ever before, unlocking answers about our universe that have been out of reach for centuries.
International Collaboration and Beyond
While commercial initiatives are driving innovation, international collaboration remains a cornerstone of space exploration. The ISS, a symbol of unity among nations, continues to serve as a platform for scientific research and technological advancements. As we venture further into the cosmos, collaboration between space agencies and private enterprises will be vital to our collective progress.
Conclusion
The retirement of the Space Shuttle program marked the end of an era in space transportation. Despite their remarkable achievements, the high costs and risks associated with the Space Shuttle fleet led NASA to seek alternative solutions. The reliance on the Russian Soyuz spacecraft demonstrated both the importance of international collaboration and the need for NASA to develop its own capabilities.
As we witness the rise of commercial spaceflight and the development of new spacecraft, the future of space transportation holds immense promise. From the Soyuz to Starships, humanity’s journey into space continues to captivate our imagination and push the boundaries of what we can achieve. As we embark on this new chapter, let us embrace the spirit of exploration and collaboration that has propelled us to where we are today.
Additional Information:
- The retirement of the Space Shuttle program opened up opportunities for commercial spaceflight companies to enter the market.
- The Commercial Crew Program aims to reduce reliance on foreign spacecraft and foster a competitive commercial space industry within the United States.










Sharing is caring!